Tonsillitis
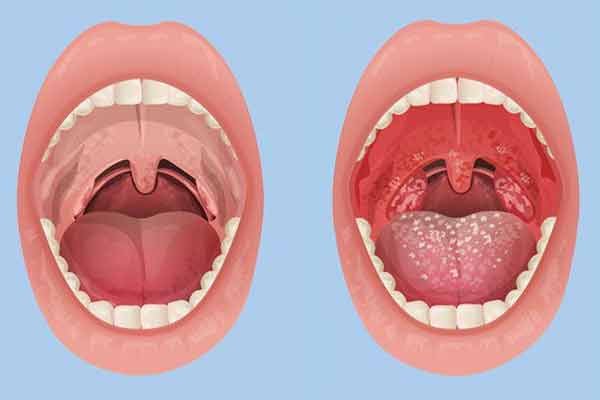
Causes of Tonsillitis:
Symptoms of Tonsillitis: The symptoms of tonsillitis can vary depending on the individual and the underlying cause. Common signs and symptoms include:
Sore throat: Tonsillitis typically presents with a severe sore throat, which may be accompanied by pain while swallowing or talking.
Swollen tonsils: The tonsils appear red and swollen, and may have a white or yellow coating of pus.
Difficulty swallowing: The inflamed tonsils can make swallowing food and liquids painful and challenging.
Ear pain: Tonsillitis can cause referred pain to the ears, leading to discomfort.
Bad breath: Foul-smelling breath can occur due to the accumulation of bacteria and debris in the tonsils.
Fever: In bacterial tonsillitis, a high-grade fever may be present, while viral tonsillitis may be associated with a low-grade fever.
Fatigue: Tonsillitis can cause fatigue and general malaise, making it difficult to carry out daily activities.
