Chronic Joint Problems
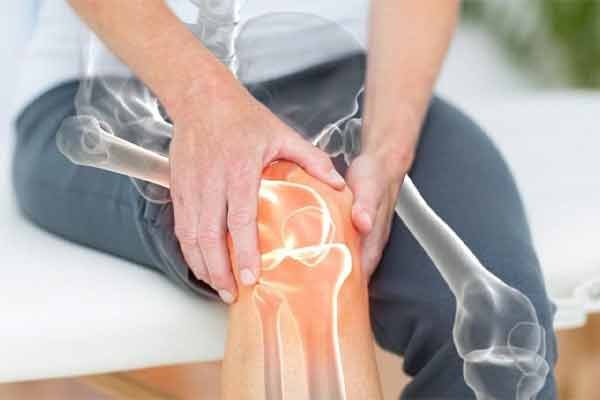
Common Types of Chronic Joint Problems:
Osteoarthritis: The most prevalent form of chronic joint disease, osteoarthritis occurs when the protective cartilage covering the ends of bones wears down over time, leading to joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. It commonly affects weight-bearing joints such as the knees, hips, and spine.
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Unlike osteoarthritis, rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disorder where the immune system mistakenly attacks the joints, causing chronic inflammation. It commonly affects the small joints of the hands and feet and can lead to joint deformity and systemic complications.
Gout: Gout is a form of inflammatory arthritis caused by the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. It typically affects the big toe, causing intense pain, redness, and swelling. Gout flares are often recurrent and can be triggered by dietary factors.
Psoriatic Arthritis: Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic inflammatory condition that affects individuals with psoriasis, a skin disorder. It involves joint inflammation, stiffness, and swelling, and can also affect the skin, nails, and other organs.
Ankylosing Spondylitis: Ankylosing spondylitis primarily affects the spine, causing chronic inflammation that can lead to stiffness, reduced flexibility, and fusion of the vertebrae. It often begins in early adulthood and may affect other joints as well.